What is Diabetes?
Most of the food that we consume is broken down into glucose. Various hormones regulate blood glucose levels; most important among them is insulin. Insulin is essential to maintain blood glucose within normal limits. With the help of insulin body tissues utilize glucose. When glucose level in the blood increases, insulin is produced and it brings back the glucose to normal levels. The blood sugar levels drop as soon as the glucose enters the cells.
However, a person with diabetes is affected with hyperglycemia, a medical condition of an elevated glucose level (>160mg/dl). The increased glucose level may be due to the following reasons:
- Insufficient insulin production by pancreas
- Improper uptake of the glucose by cells due to Insulin resistance

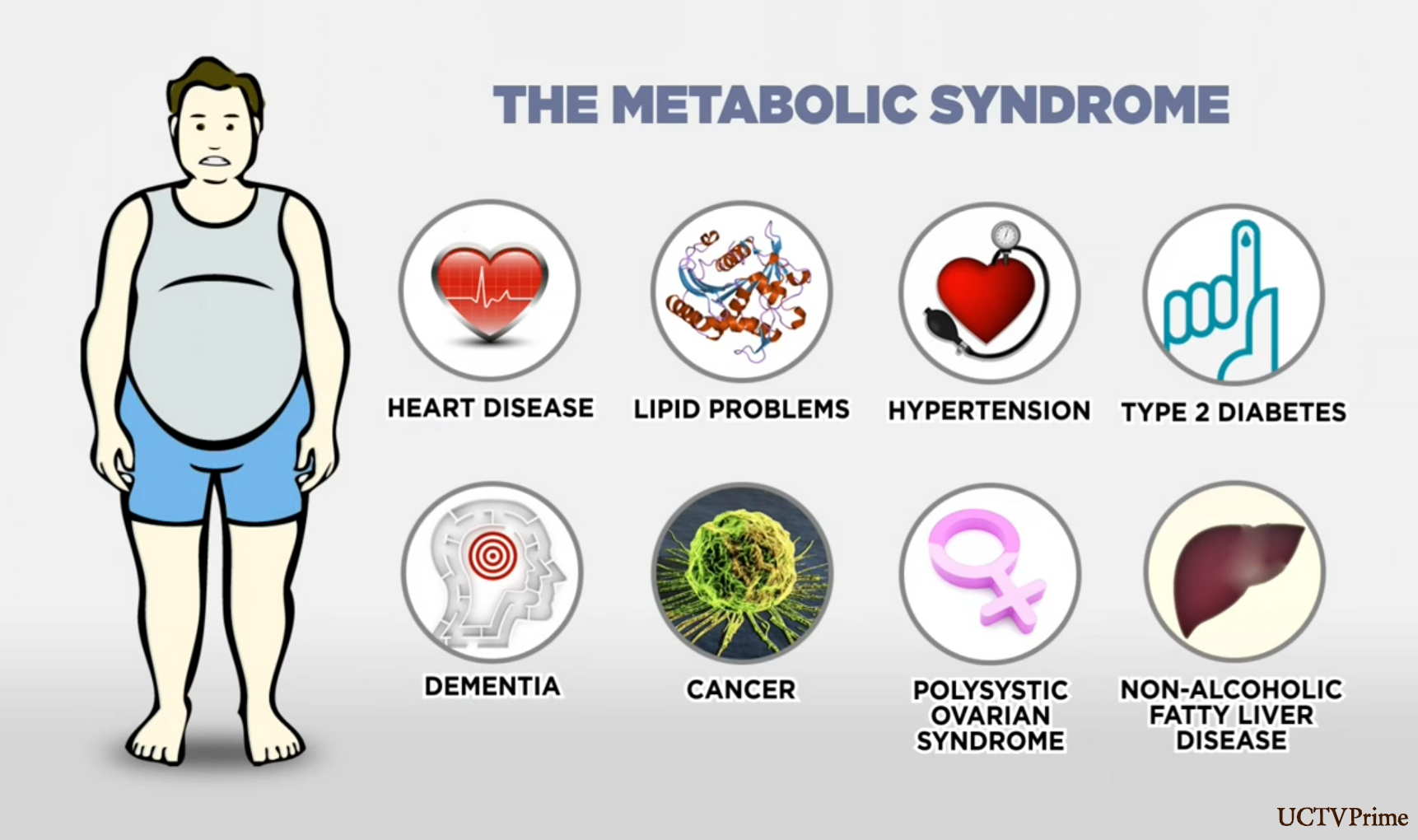
What is Metabolic Syndrome?
Metabolic syndrome is the name for a group of risk factors that increases your chance of developing heart disease, hypertension, diabetes, dyslipidemia and stroke.
You must have at least three metabolic risk factors to be diagnosed with metabolic syndrome.
- A large waistline indicating abdominal (Truncal) obesity.
- A high triglyceride level. Triglycerides are a type of fat found in the blood.
- A low HDL cholesterol level. HDL sometimes is called “good” cholesterol. This is because it helps remove cholesterol from your arteries. A low HDL cholesterol level raises your risk for heart disease.
- High blood pressure
- High fasting blood sugar
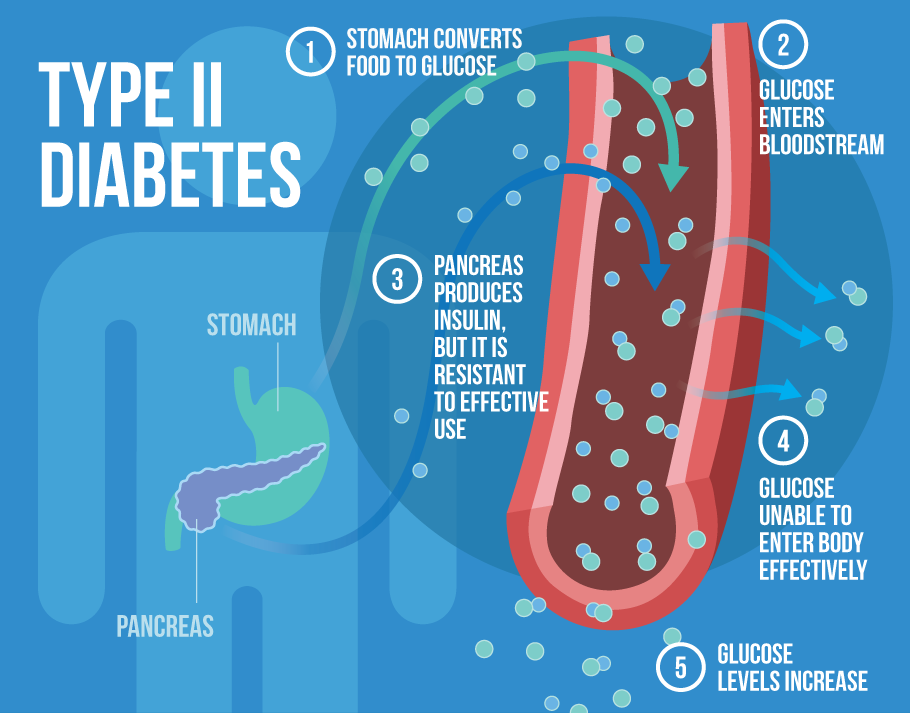
What is Type 2 Diabetes?
Diabetes mellitus, often simply referred to as diabetes, is a disease in which a person has high blood sugar, either because the body does not produce enough insulin, or because cells do not respond to the insulin that is produced.
There are two main types of diabetes.
- Type 1 diabetes results from the body’s failure to produce insulin, and presently requires the person to inject insulin lifelong. It is commonly seen in children.
- Type 2diabetes results from insulin resistance, a condition in which cells fail to use insulin properly, sometimes combined with an absolute insulin deficiency. This is the most common form of diabetes, accounting 90% of diabetes patients. Type 2 diabetes is diagnosed by demonstrating any one of the following:
- Fasting plasma glucose level ≥ 126 mg/dL.
- Plasma glucose ≥ 200 mg/dL two hours after a 75 g oral glucose load as in a glucose tolerance test.
- Symptoms of hyperglycemia and random plasma glucose ≥ 200 mg/dL.
- Glycated hemoglobin (Hb A1C) ≥ 6.5%.
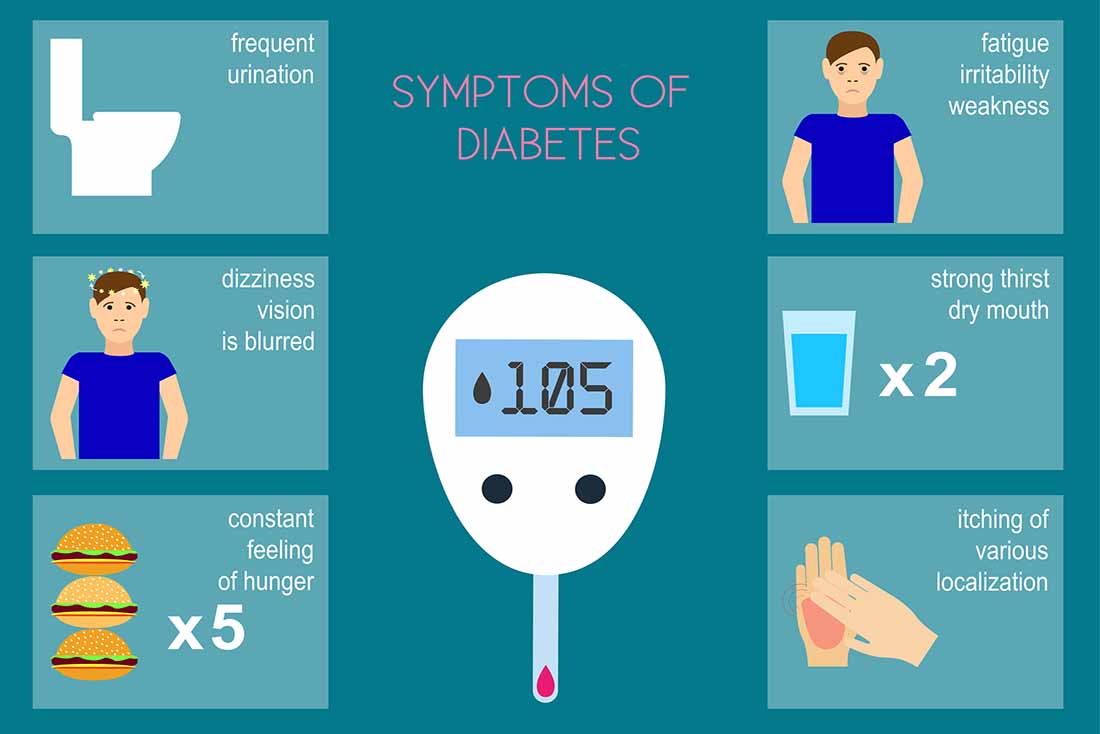
What will be the symptoms of Diabetes?
- Polyuria: This condition corresponds to the increased frequency & amount of urine. The volume of urine excreted during this condition is above 3litre per day.
- Slow healing: Appropriate healing is a process that requires a proper immune response over a period of time.
- Polydipsia: The excessive tendency to drink water is known as polydipsia. Frequent dryness of the mouth is the main reason for this.
- Polyphagia: Also known as hyperphagia, the condition refers to increased sensation to eat more often.
- Blurred vision: Any deviation from the normal sharpness of vision is called blurred vision.
- Fatigue: When a person is affected with diabetes, extreme tiredness may be experienced even after having the required amount of rest.
- Weight loss: A sudden and unexplained weight loss can be due to the prevalence of diabetes in an individual.
- Itchy sensation in the genitalia.

Type 2 Diabetes without proper treatments can cause many serious long-term complications. These include:
Diabetic Retinopathy – the leading cause of blindness in adults.
Diabetic Nephropathy – the leading cause of kidney failure in adults.
Diabetic Neuropathy – leading cause of non-traumatic amputations of the lower extremities in adults.
Cardiovascular disease – 8/10 patients with type 2 diabetes die of cardiovascular disease.
Stroke – 2 to 4 times more likely to have a stroke.
What is Metabolic Surgery?
In 2009 the American Society for Bariatric Surgery (ASBS) changed its name to the American Society for Metabolic and Bariatric Surgery (ASMBS) to promote information on the beneficial effects of surgeries for weight loss in treating metabolic diseases, especially Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus (T2DM).
Today, the term Metabolic Surgery is used to describe surgical procedures to treat metabolic diseases, especially, type 2 diabetes.
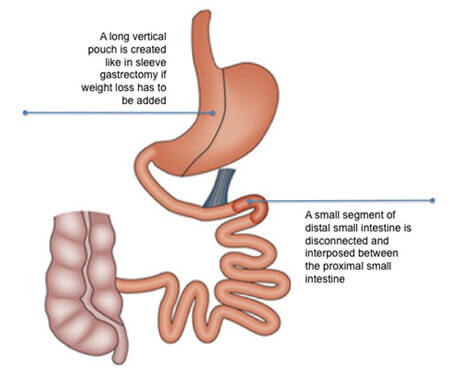

Metabolic Surgery for Type 2 Diabetes
In this form of diabetes, the body does not produce enough of the insulin, or the cells in the body do not use insulin properly. Insulin is necessary for the body to be able to use blood sugar for energy. As a result, glucose builds up in the blood, instead of going into cells. Type 2 diabetes is the form of the disease most closely linked to obesity and the name Diabesity has been used to describe this association.
How Type 2 Diabetes is medically treated?
Traditional 1st line treatment includes losing excess weight, eating a healthful diet and engaging in regular exercise. When these modifications do not make enough control in the disease, medications can be prescribed. Some medications help the pancreas produce more insulin; while others help the body to use the insulin that was produced efficiently. If these drugs don’t work, a person needs to take insulin.
Often these traditional treatments for diabetes do not work and patients run the risks of long term complications.
Even with good medical control diabetes, some patients still go on dialysis, lose limbs, and have significant heart attacks, drug reactions and other complications. The notion that medical therapy is without risk is absolutely incorrect.
Does Metabolic Surgery “Cure” Diabetes?
Till date, diabetes is poorly understood and medical treatment cannot claim a “Cure”. The aim is to put it in remission, defined as normal blood sugar levels and no need for diabetes medication. This means bringing glucose to normal levels and arresting the progression of the diabetic complications, thus giving the body a chance to repair the damage.
In 2004, study in Journal of the American Medical Association (JAMA) of more than 22,000 people who underwent bariatric surgery showed the following:
- Diabetes was completely resolved or improved in 86% of patients.
- High blood lipids improved in 70% or more of patients.
- High blood pressure was resolved or improved in 78% of patients.
How Does Metabolic Surgery “Cure” Type 2 Diabetes?
After Metabolic surgery, remission is observed in the days to weeks before any substantial weight loss has occurred. Metabolic surgery cures Type 2 diabetes by causing calorie restriction, hormonal changes such as reduced Ghrelin, increased GLP1 and peptide YY. These hormones stimulate beta cells in pancreas to stimulate increased secretion of insulin, provided enough beta cell mass is still present in pancreas. Persistent increased GLP-1 secretion increases beta cell mass in the long term.
Before recommending any patient for metabolic surgery, evaluation of pancreatic Beta cell function is done to access Insulin secretion, Insulin Sensitivity and Insulin resistance. Type of Metabolic procedure is chosen depending on the duration of diabetes, dosage and duration of Insulin therapy, pancreatic Beta cell function, Insulin sensitivity and Insulin resistance.

How about metabolic surgery in type 2 diabetic patients who are not morbidly obese?
Actually, 2/3 of the world’s type 2 diabetics are not morbidly obese. They are however, overweight with BMI range 27-35Kg/m2. According to IDF guidelines for Asians, most of metabolic surgeons will accept patients with type 2 diabetes and BMI of 27.5Kg/m2 or greater for metabolic surgery.
It is possible that metabolic surgery may benefit even person with diabetes who are not overweight or obese.


